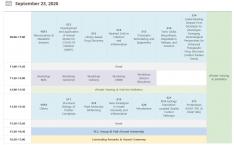
Angiopoietin (Angpt)-Tie receptor 2 (Tie2) plays key roles in vascular development and homeostasis as well as pathological vascular remodeling. Therefore, Tie2-agonistic antibody and engineered Angpt1 variants have been developed as potential therapeutics for ischemic and inflammatory vascular diseases. However, their underlying mechanisms for Tie2 clustering and activation remain elusive and the poor manufacturability and stability of Angpt1 variants limit their clinical application. Here, we develop a human Tie2-agonistic antibody (hTAAB), which targets the membrane proximal fibronectin type III domain of Tie2 distinct from the Angpt-binding site. Our Tie2/hTAAB complex structures reveal that hTAAB tethers the preformed Tie2 homodimers into polygonal assemblies through specific binding to Tie2 Fn3 domain. Notably, the polygonal Tie2 clustering induced by hTAAB is critical for Tie2 activation and are resistant to antagonism by Angpt2. Our results provide insight into the molecular mechanism of Tie2 clustering and activation mediated by hTAAB, and the structure-based humanization of hTAAB creates a potential clinical application.
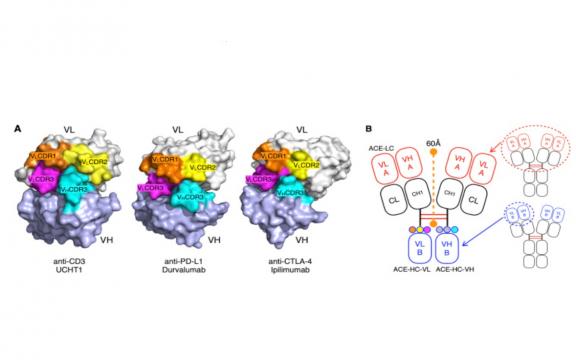
Following the clinical success of immunotherapeutic antibodies, bispecific antibodies for cytotoxic effector cell redirection, tumor-targeted immunomodulation and dual immunomodulation, have received particular attentions. Here, we developed a novel bispecific antibody platform, termed Antibody-Like Cell Engager (ALiCE), wherein the Fc domain of each heavy chain of immunoglobulin G (IgG) is replaced by the VH and VL domains of an IgG specific to a second antigen while retaining the N-terminal Fab of the parent antibody. Because of specific interactions between the substituted VH and VL domains, the C-terminal stem Fv enables ALiCE to assemble autonomously into hetero-tetramers, thus simultaneously binding to two distinct antigens but with different avidities. This design strategy was used to generate ACE-05 (two anti-PD-L1 Fab × anti-CD3 Fv) and ACE-31 (two anti-CD3 Fab × anti-PD-L1 Fv), both of which bound PD-L1 and CD3. However, ACE-05 was more effective than ACE-31 in reducing off-target toxicity caused by the indiscriminate activation of T cells. Moreover, in cell-based assays and PBMC-reconstituted humanized mice harboring human non-small-cell lung cancer tumors, ACE-05 showed marked antitumor efficacy, causing complete tumor regression at a dose of 0.05 mg/kg body weight. The dual roles of ACE-05 in immune checkpoint inhibition and T-cell redirection, coupled with reduced off-target toxicity, suggest that ACE-05 may be a promising anti-cancer therapeutic agent. Moreover, the bispecific ALiCE platform can be further used for tumor-targeted or multiple immunomodulation applications.
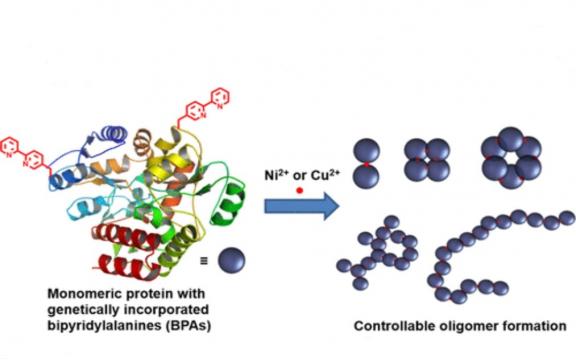
Many natural proteins function in oligomeric forms, which are critical for their sophisticated functions. The construction of protein assemblies has great potential for biosensors, enzyme catalysis, and biomedical applications. In designing protein assemblies, a critical process is to create protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks at defined sites of a target protein. Although a few methods are available for this purpose, most of them are dependent on existing PPIs of natural proteins to some extent. In this report, a metal-chelating amino acid, 2,2′-bipyridylalanine (BPA), was genetically introduced into defined sites of a monomeric protein and used to form protein oligomers. Depending on the number of BPAs introduced into the protein and the species of metal ions (Ni2+ and Cu2+), dimers or oligomers with different oligomerization patterns were formed by complexation with a metal ion. Oligomer sizes could also be controlled by incorporating two BPAs at different locations with varied angles to the center of the protein. When three BPAs were introduced, the monomeric protein formed a large complex with Ni2+. In addition, when Cu2+ was used for complex formation with the protein containing two BPAs, a linear complex was formed. The method proposed in this report is technically simple and generally applicable to various proteins with interesting functions. Therefore, this method would be useful for the design and construction of functional protein assemblies.
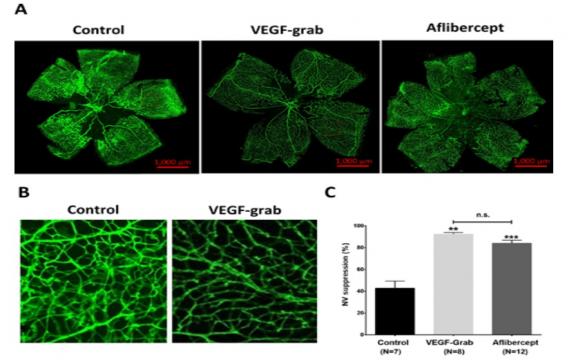
Methods: The in vitro anti-VEGF efficacy of VEGF-Grab was determined using VEGF-induced cell proliferation/migration and tube formation assays. The in vivo antiangiogenic efficacy of intravitreal injection of either VEGF-Grab or aflibercept was evaluated using murine models of ocular angiogenesis: mouse oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) and rat laser-induced choroidal neovascularization (CNV). The in vivo retinal toxicity in the mouse eye resulting from the injection of either drug was evaluated with light and electron microscopy.
Results: VEGF-Grab showed greater inhibition of VEGF-induced cell proliferation/migration than aflibercept, but it showed comparable inhibition of tube formation in vitro. In the in vivo OIR model, VEGF-Grab showed a comparable suppression of retinal neovascularization compared to aflibercept. Additionally, VEGF-Grab showed an efficacy similar to that of aflibercept in terms of CNV inhibition in the laser-induced CNV model. Histology and transmission electron microscopy showed no significant signs of toxicity in the mouse retina at 7 and 30 days following the intravitreal injection of VEGF-Grab or aflibercept.
Conclusions: Compared to aflibercept, VEGF-Grab presented comparable in vivo antiangiogenic efficacy and superior in vitro anti-VEGF activity. The retinal safety profiles were comparable for the two drugs. Considering its known higher binding affinity to VEGF and PlGF compared to aflibercept, VEGF-Grab could be a potential candidate drug for neovascular retinal diseases and an alternative to aflibercept.
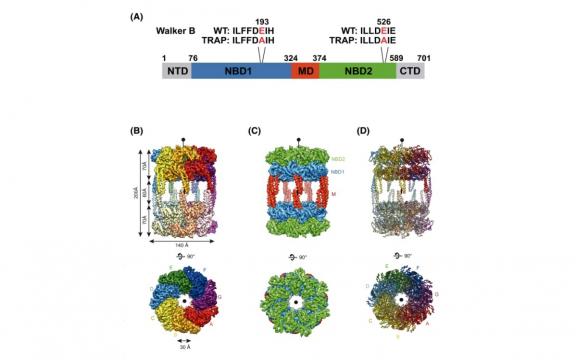
AAA+ (ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities) chaperones are involved in a plethora of cellular activities to ensure protein homeostasis. The function of AAA+ chaperones is mostly modulated by their hexameric/dodecameric quaternary structures. Here we report the structural and biochemical characterizations of a tetradecameric AAA+ chaperone, ClpL from Streptococcus pneumoniae. ClpL exists as a tetradecamer in solution in the presence of ATP. The cryo-EM structure of ClpL at 4.5 Å resolution reveals a striking tetradecameric arrangement. Solution structures of ClpL derived from small-angle X-ray scattering data suggest that the tetradecameric ClpL could assume a spiral conformation found in active hexameric/dodecameric AAA+ chaperone structures. Vertical positioning of the middle domain accounts for the head-to-head arrangement of two heptameric rings. Biochemical activity assays with site-directed mutagenesis confirmed the critical roles of residues both in the integrity of the tetradecameric arrangement and activities of ClpL. Non-conserved Q321 and R670 are crucial in the heptameric ring assembly of ClpL. These results establish that ClpL is a functionally active tetradecamer, clearly distinct from hexameric/dodecameric AAA+ chaperones.
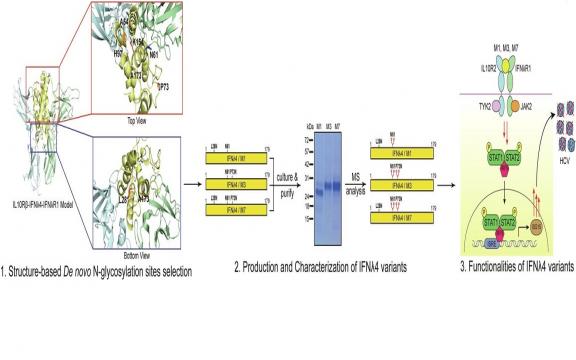
Interferon lambda 4 (IFNλ4) has been recently known and studied for its role in hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, but its clinical potential is significantly hampered due to its poor expression in vitro. Our study reports the successful production of IFNλ4 from a mammalian cell line through a glycoengineering and structure-based approach. We introduced de novo N-glycosylation of IFNλ4, guided by structural analysis, and produced IFNλ4 variants in Expi293F that displayed improved expression and potency. To preserve the structure and functionality of IFNλ4, the model structure of the IFNλ4 signaling complex was analyzed and the N-glycosylation candidate sites were selected. The receptor binding activity of engineered IFNλ4 variants and their receptor-mediated signaling pathway were similar to the E. coli version of IFNλ4 (eIFNλ4), while the antiviral activity and induction levels of interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) were all more robust in our variants. Our engineered IFNλ4 variants may be further developed for clinical applications and utilized in basic research to decipher the immunological roles of IFNλ4.
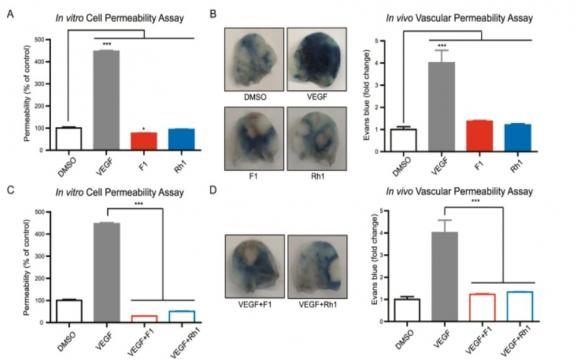
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays a key role in angiogenesis, but VEGF-induced angiogenesis is often accompanied by a vascular permeability response. Ginsenosides are triterpenoid saponins from the well-known medicinal plant, ginseng, and have been considered a candidate for modulating angiogenesis. Here, we systemically investigated the effects of 10 different ginsenosides on human umbilical vein endothelial cells and newly identified that two PPT-type ginsenosides, F1 and Rh1 induce the migration and proliferation of endothelial cells. Interestingly, RNA transcriptome analysis showed that gene regulation induced by VEGF in endothelial cells is distinct from that of ginsenoside F1 and Rh1. In addition, F1 and Rh1 significantly inhibited vascular leakage both in vitro and in vivo, which are induced by vascular endothelial growth factor. Furthermore, comparative transcriptome analysis revealed that these effects of F1 and Rh1 on vascular leakage restoration are mainly caused by changes in VEGF-mediated TNFα signaling via NFκB, particularly by the suppression of expression and transcriptional activity of NR4A1 by F1 and Rh1, even in the presence of VEGF. These findings demonstrate that ginsenosides F1 and Rh1 can be a promising herbal remedy for vessel normalization in ischemic disease and cancer and that NR4A1 is the key target.
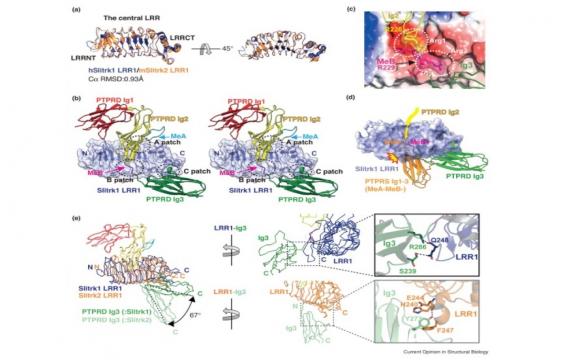
Slit-like and Trk-like (Slitrk) family members are leucine-rich repeat (LRR)-containing neuronal transmembrane proteins. Slitrks have been highlighted as key synapse organizers at neuronal synapses through interactions with specific members of the presynaptic type IIa receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase (RPTP) family. Recent structural studies on type IIa RPTP/Slitrk1 complexes have unveiled molecular insights into their binding selectivity and have established the role of higher-order receptor clustering in their synaptogenic activity. Here, we will discuss key structural aspects of Slitrk interactions with type IIa RPTP family members, the biological roles of Slitrks in neurons, and our current knowledge of SLITRK mutations in human diseases.
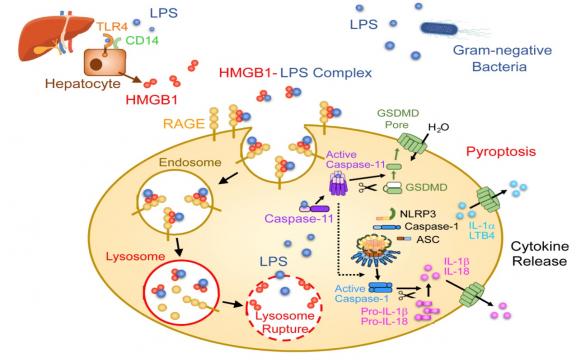
Recognition of cytoplasmic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) by caspase-11 leads to pyroptosis and secretion of inflammatory mediators. In this issue of Immunity, Deng et al. (2018) report that high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) secreted by hepatocytes delivers extracellular LPS into the cytoplasm and mediates pyroptosis.
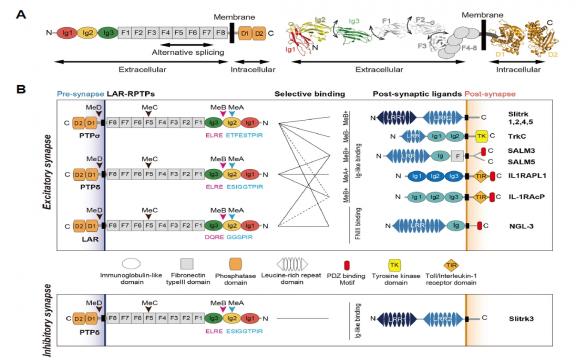
Leukocyte common antigen-related protein tyrosine phosphatases (LAR-RPTPs) are cellular receptors of heparan sulfate (HS) and chondroitin sulfate (CS) proteoglycans that regulate neurite outgrowth and neuronal regeneration. LAR-RPTPs have also received particular attention as the major presynaptic hubs for synapse organization through selective binding to numerous postsynaptic adhesion partners. Recent structural studies on LAR-RPTP?mediated trans-synaptic adhesion complexes have provided significant insight into the molecular basis of their specific interactions, the key codes for their selective binding, as well as the higher-order clustering of LAR-RPTPs necessary for synaptogenic activity. In this review, we summarize the structures of LAR-RPTPs in complex with various postsynaptic adhesion partners and discuss the molecular mechanisms underlying LAR-RPTP?mediated synaptogenesis.
Research Group
Publication
A dynamic substrate pool revealed by cryo-EM of a lipid-preserved respiratory supercomplex Tae Jin Jeon, Seong-Gyu Lee, Suk Hyun Yoo, Myeongbin Kim, Dabin Song, Joong Hyun Ryu, Hwangseo Park, Deok Soo Kim, Jaekyung Hyun, Ho ...
Structural insights into the clustering and activation of Tie2 receptor mediated by Tie2 agonistic... Gyunghee Jo, Jeomil Bae, Ho Jeong Hong, Ah-Reum Han, Do-Kyun Kim, Seon Pyo Hong, Jung A Kim, Sangkyu Lee, Gou Young Koh, Ho Min Kim.&...
High-yield synthesis and purification of recombinant human GABA transaminase for high-throughput s... Mingu Gordon Park, Ah-Reum Han, Su Yeon Kim, Tai Young Kim, Ho Min Kim, C Justin Lee. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021. 36(...
Soluble Fas ligand drives autoantibody-induced arthritis by binding to DR5/TRAIL-R2. Dongjin Jeong, Hye Sung Kim, Hye Young Kim, Min Jueng Kang, Hyeryeon Jung, Yumi Oh, Donghyun Kim, Jaemoon Koh, Sung-Yup Cho, Yoon Kyu...
Job Openings

- 2021-5회 바이오분자 및 세포 구조 연구단 단백질 커뮤니케... 2022-01-18
- 2021-4회 바이오분자 및 세포 구조 연구단 단백질 커뮤니케... 2022-01-18