STARK (Silicon Telescope Array for Reaction studies in inverse Kinematics)
1. Motivation
- One of the powerful experimental method to study nuclear reactions
- An ejectile reflects the properties of residual nucleus
- Measure energy, angular momentum, cross-section, spectroscopic factor
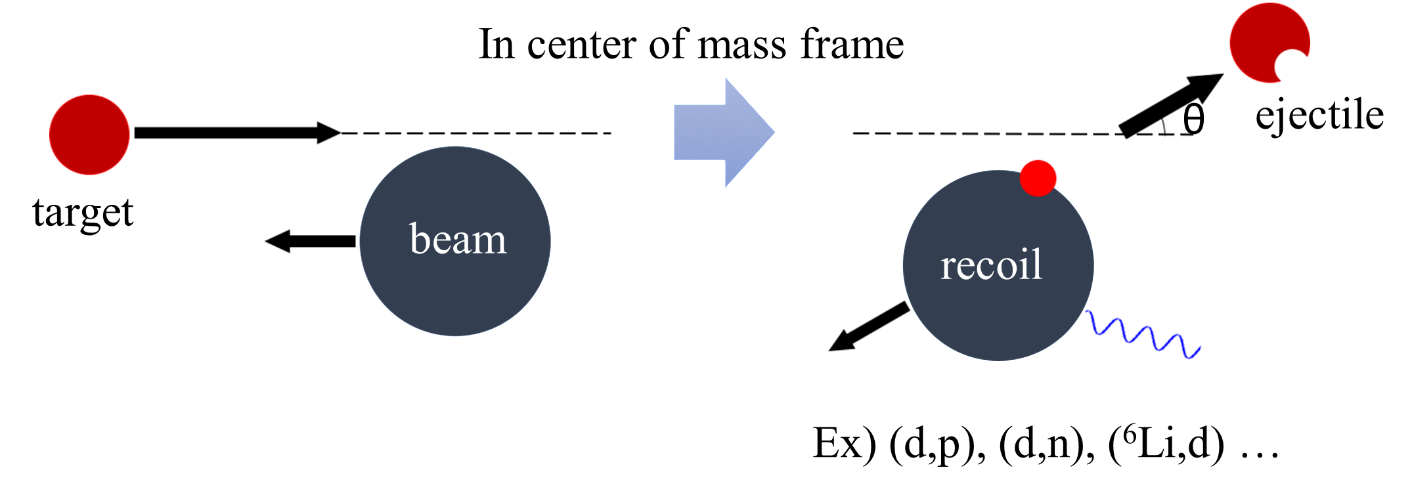
Schematic overview of the transfer reaction
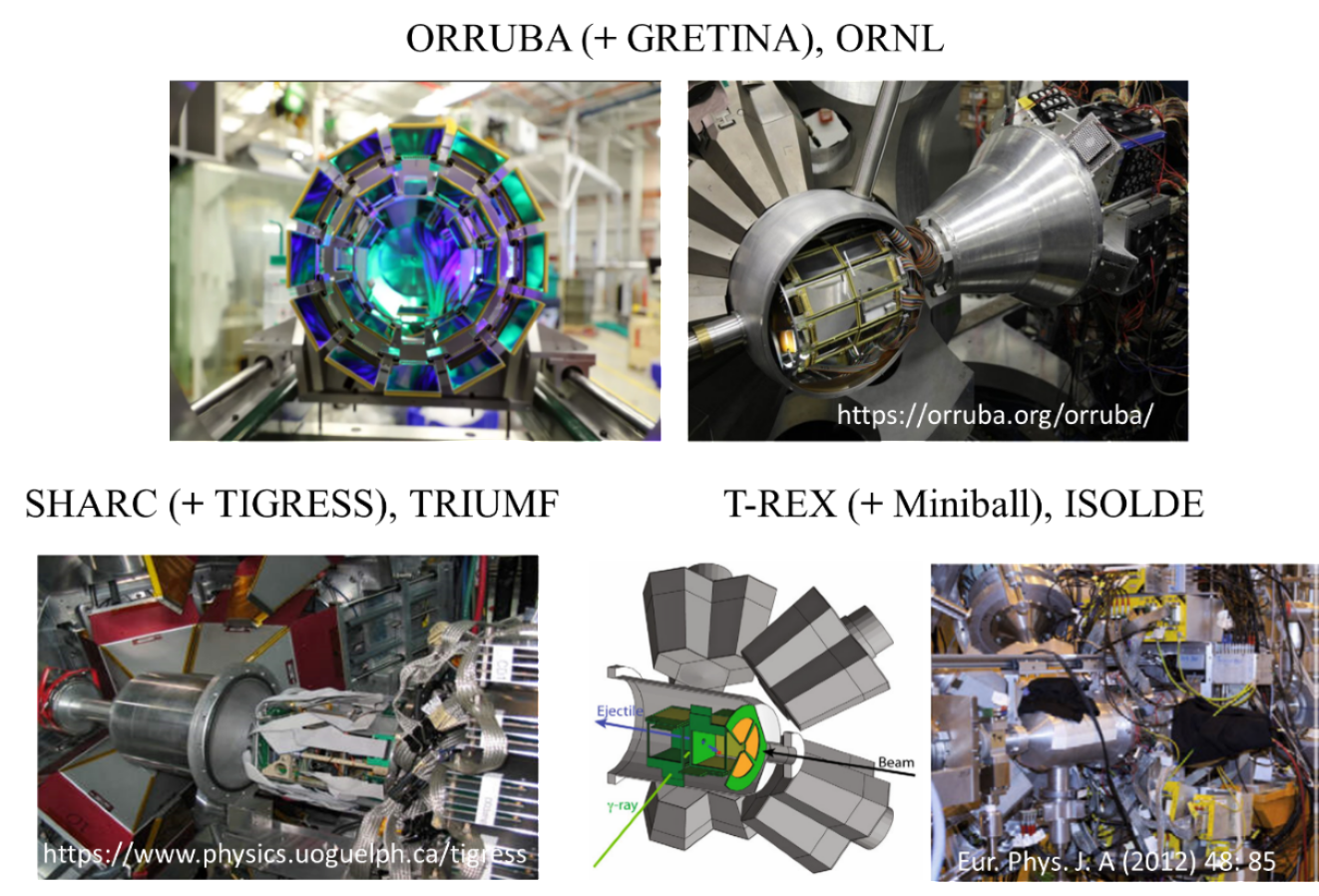
Silicon telescope array for reaction studies in the world
2. Detector design
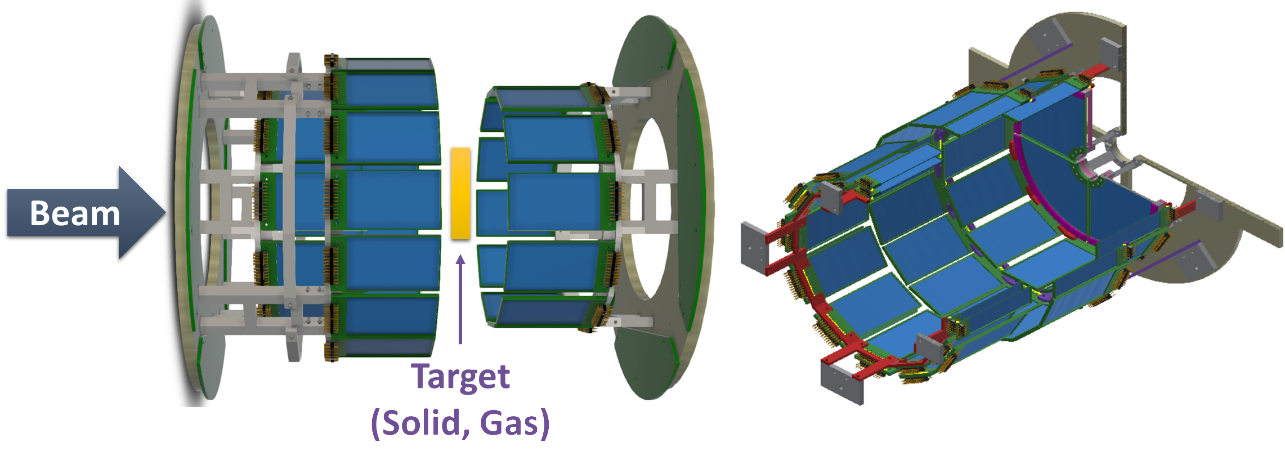
STARK conceptual design
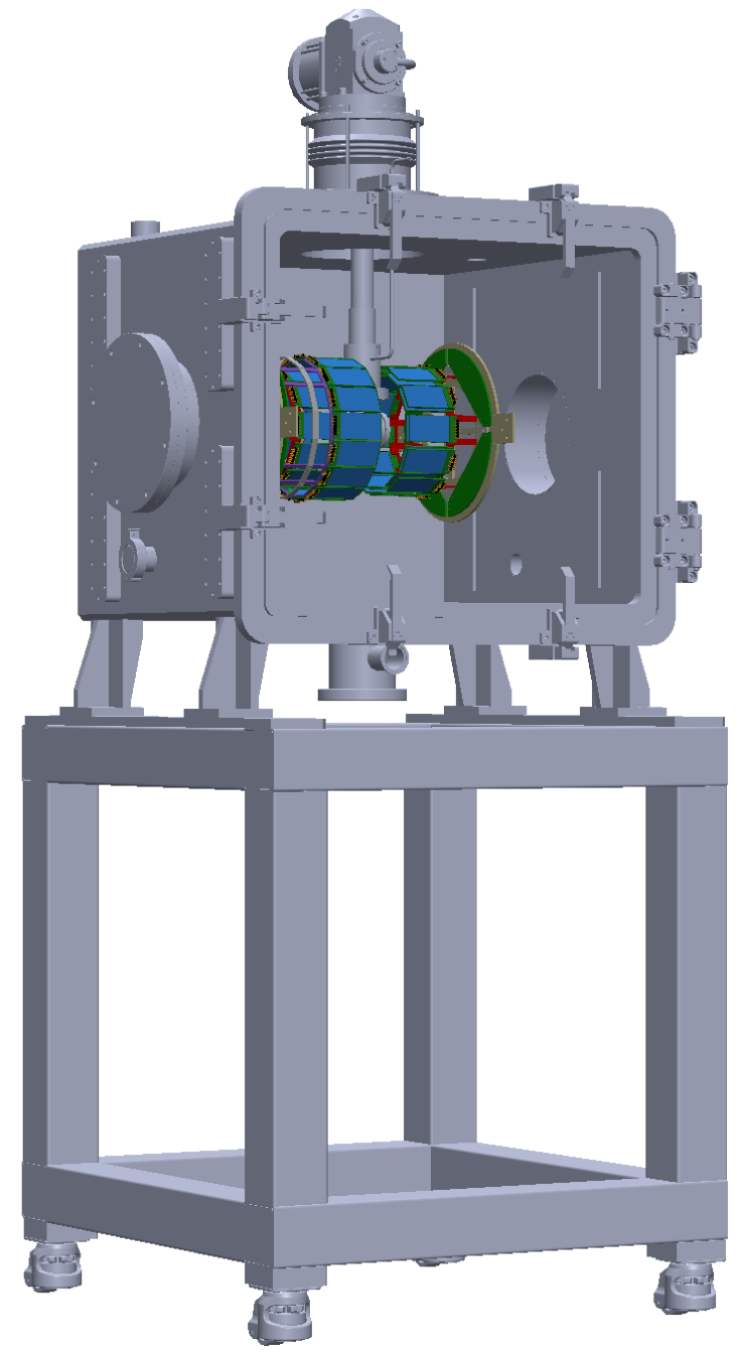
STARK design with a cryogenic gas cell chamber
- Charged particle detection from collision (E,p)
- Barrel type array, 12 + 16 + 12 sided ring
- Φ = 92.5, 118.8, 107 mm, 28.4 mm gap for target
- Δθlab < 1˚ expected with wide coverage (43˚ ~ 78˚, 105˚ ~ 150˚) => Comparable or better than
state-of-the-art detectors
- Newly designed resistive silicon strip detector, X6
- Useful for many rare isotope facilities (ex. RIKEN, FRIB and RAON)
3. Detector specification
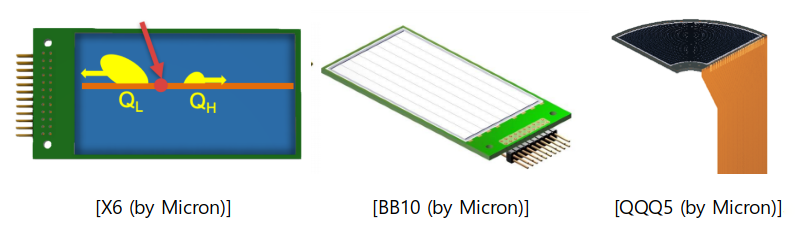
- Junction side : 8 resistive strips, 5.6 mm pitch (2 read-outs)
- Ohmic side : 4 normal strips
- Active area : 75 × 40.3 mm2 (1 mm thickness)
- Position : (QH – QL) / (QH + QL) ~ 1 mm resolution expected
- Energy : (QH + QL)
4. Detector performance test
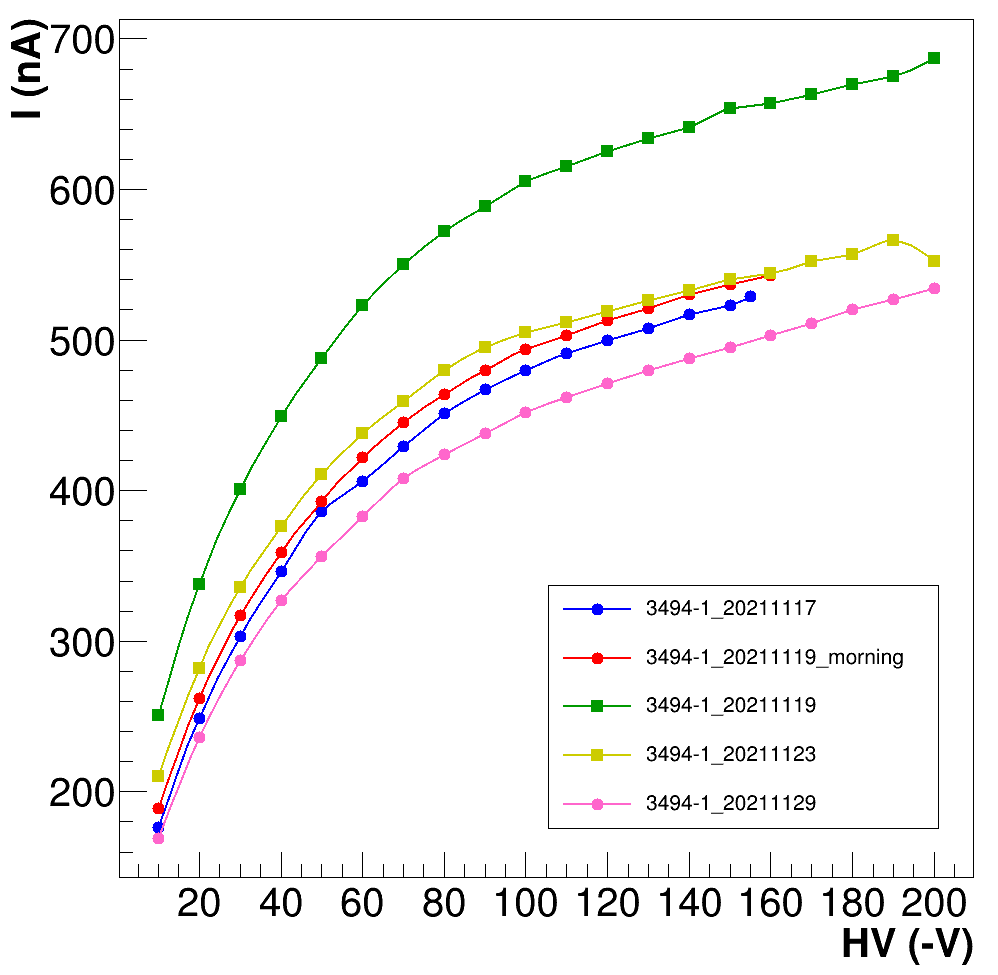
Depletion voltage test
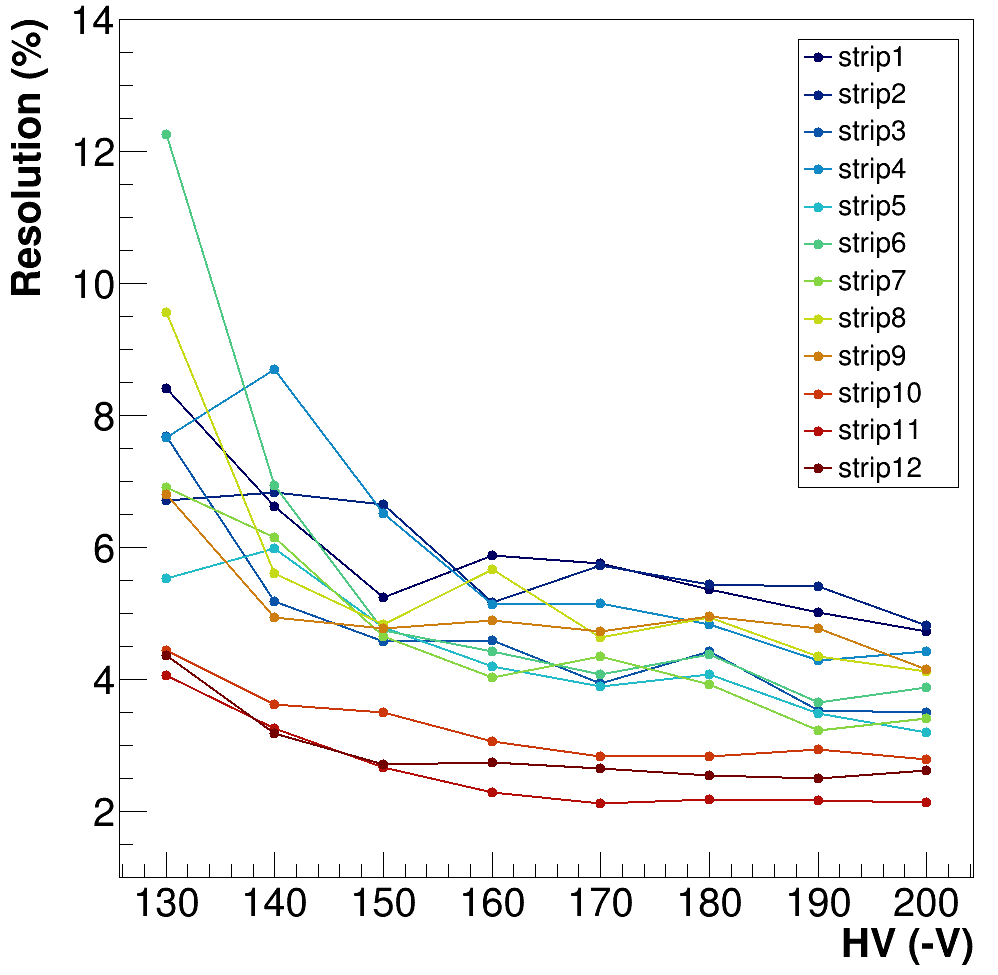
Resolution test
5. Current status & future plan
- X6 detector is arrived and testing the performance
- Assembly structure was delivered
- Preparing electronics for DAQ system
- Detector and DAQ test on 2022
- System commissioning on 2023
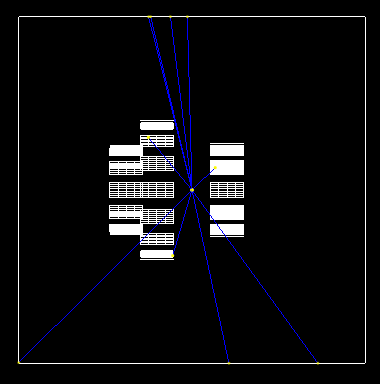
Geant4 simulation
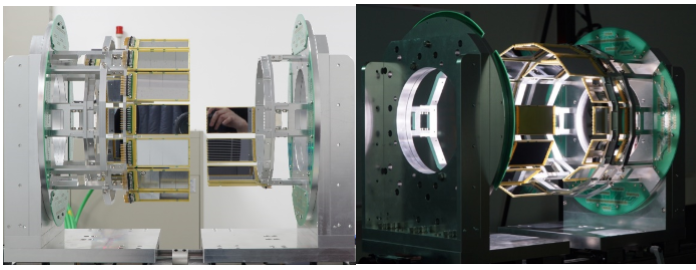
STARK assembly
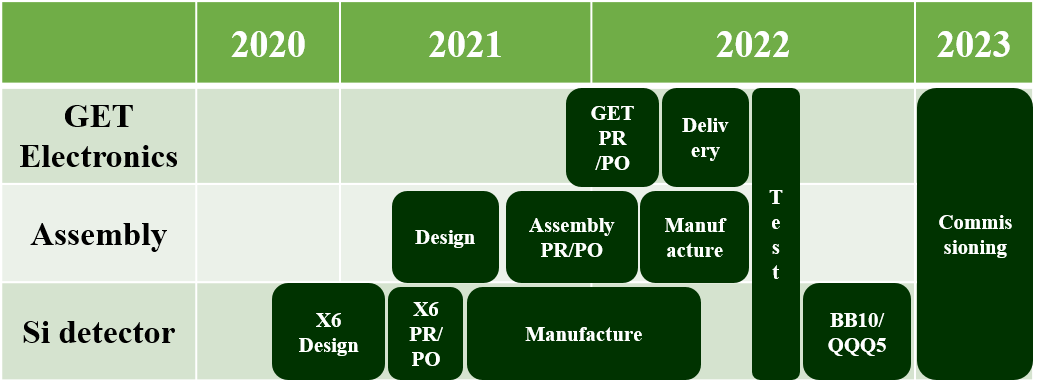
Future plan










